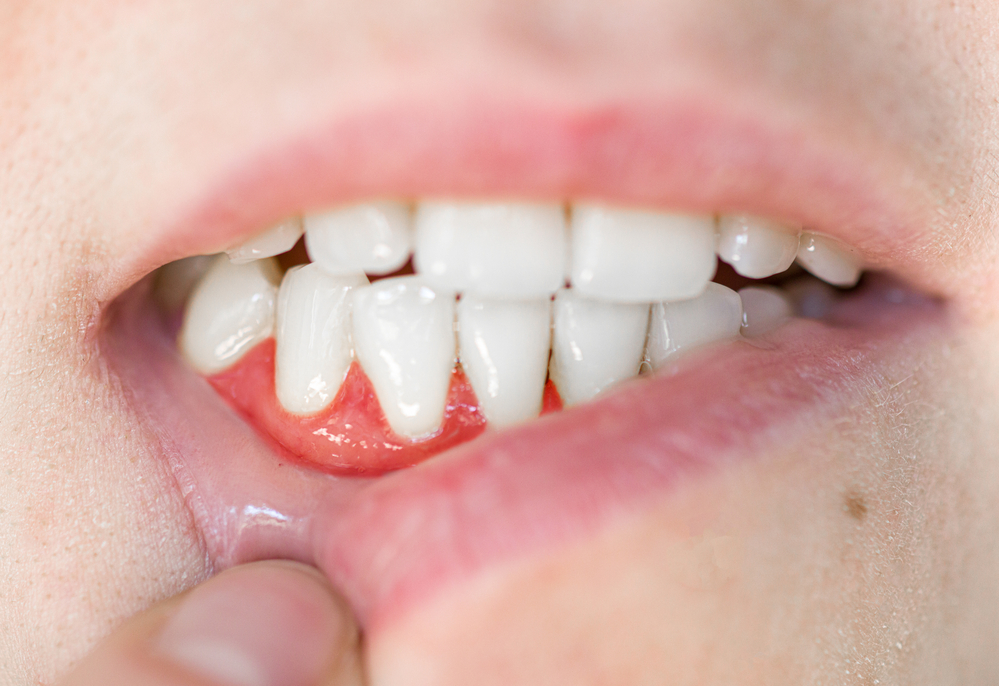
What is Gum Recession?
Gum recession is a dental condition characterized by the root of a tooth or teeth being exposed because the gum line has receded or pulled away.
Gum line recession doesn’t happen overnight. It is a gradual occurrence unnoticeable for years and is mostly common in adults over 40 years of age. However, the condition can also affect young people below 40.
Signs of Receding Gums: How Do I Know I Have Gum Line Recession?
Gum line recession exhibits the following main signs:
- Longer-looking teeth: An initial change in appearance is the most obvious sign linked to loss of gum tissue, which makes teeth look longer than natural. This sign is usually accompanied by an uneven gum line, a small notch/bump above the gum line, and/or plaque retention.
- Tooth sensitivity: The condition exposes the teeth root (usually covered by the gums), resulting in sensitivity to hot/cold foods/drinks, touch, brushing, etc.
- Tooth mobility/loss: Gum recession can cause the teeth to move and fall in some cases if the condition isn’t treated.
Gum Recession Causes
There are several causes of gum line recession, the most notable being:
1. Poor Dental Care
Failing to brush and floss properly daily can cause bacteria buildup on the gumline, resulting in dental infections that wear off the teeth root and gums.
2. Periodontal Disease (Gum Disease)
Periodontal diseases like gingivitis (that affects the gums and bone responsible for supporting teeth) can also cause gingival recession[1].
3. Poor Oral Cleaning Techniques (Over-brushing)
If you use hard-bristled toothbrushes and/or overbrush your teeth, you can erode teeth enamel, causing gum line recession. Aggressive brushing can also irritate gum tissue, causing the same problem.
4. Genetics
Some people are also genetically predisposed to thin gum tissue, which increases their odds of suffering from gum line recession[2].
5. Lifestyle Habits
Habits such as tobacco use can increase the likelihood of gum recession by increasing plaque buildup risks on the gingival lining[3].
6. Teeth Grinding & Clenching
The forces involved when grinding and clenching teeth can weaken structures such as the gums and alveolar bone that support the teeth[4].
7. Trauma
Mouth piercings (lip/tongue piercings) that rub against the gums can cause trauma and gum line recession over time. The same applies to trauma injury to the mouth/teeth/gums.
8. Hormonal Changes
Decreasing estrogen levels experienced during menopause can cause a loss in bone density, resulting in gum recession[5].
Will The Gum Recession Grow Back?
No! However, the condition can be stopped from worsening by dental treatments that reconstruct gum tissue. Good dental hygiene changes can help stop gum recession.
How To Stop Gum Recession
There are two main ways to stop gum recession: you can incorporate some good practices into your routine and you can also see an expert if the remedies don’t yield results.
1. Good Practices to Stop Gum Recession
From the causes of gum recession discussed above, there are some measures that you can take:
- Maintain proper oral hygiene: Gum recession linked to poor oral health can be stopped by brushing after meals and flossing once daily.
- Quit smoking/chewing tobacco: increased plaque buildup and resulting gum-line recession are linked to tobacco use, which is why quitting will stop further recession.
- Learning proper dental cleaning techniques: This remedy will stop the recession linked to overbrushing.
- Eating food rich in Vitamins C & E: Recession linked to poor gum health can be stopped by eating plenty of vegetables and fruits.
2. Get Professional Help from an Experienced Dentist
Good practices can help, but they will not entirely fix the situation. For instance, if gum line recession is linked to periodontal disease, you need to see a dentist immediately to stop the problem from advancing further.
Gingivitis, in the early, moderate, and advanced stages, comes with a high risk of tooth loss, bone decay, gum swelling, and halitosis, among other serious dental health conditions that require deep cleaning and a combination of treatments.
For gum recession treatment and other general and cosmetic dentistry treatments in Toronto, consider Annex Dentistry – a Bloor dental clinic with over 50 years of dental service to the community.
How To Prevent Receding Gums
There are some precautions that can be taken to ensure the condition never becomes a reality.
- Regular check-ups: A dentist can catch the early signs of periodontal disease, among other causes of gum line recession
- Proper dental care hygiene: Brushing after meals and flossing daily will prevent bacteria buildup responsible for kickstarting gum line recession. It also helps to learn how to brush gently using a soft-bristled toothbrush.
- Lifestyle changes: Quitting smoking will help eliminate plaque buildup linked to tobacco use. Maintaining a healthy, balanced diet will also ensure the body always has the necessary nutrients to fight dental conditions like gum disease and bone loss.
What Is the Best Treatment for Gum Recession?
The choice of the best gum recession solution is best left to dentists. When it comes to treatment, there are mainly two options:
i. Non-Surgical Gum Recession Treatment
Your dentist can offer different non-surgical treatments depending on the underlying cause:
- Orthodontic treatments like realigning teeth using braces or clear aligners can eliminate underlying causes of gum recession, like teeth clenching and grinding.
- Treatments like frenectomy can treat gum recession linked to a frenal pull.
- Replacement/adjustment of dental prosthetics can stop underlying causes like plaque accumulation.
- The application of desensitizing agents on the tooth root/s can treat sensitivity in mild gum recession cases.
- Periodontitis treatment, which includes procedures like tooth scaling, root planing, and the use of antibiotics alongside antibacterial mouthwash, can eliminate harmful bacteria behind the condition.
ii. Surgical Gum Recession Treatment
Non-surgical treatments may not always be effective in dealing with gum line recession. In such a case, surgical treatments can be employed.
a. Surgical Removal of Plaque
In advanced periodontitis, the plaque responsible for the disease can be surgically removed from a tooth’s root.
b. Gum Graft
Gum grafting can also be done to deal with the permanent natural regeneration of gums. The surgical procedure involves the removal of dental tissue (usually from the palate or roof of the mouth) and placing the tissue over the exposed tooth root. The tissue is secured using sutures before being left to heal.
For effective surgical results, the underlying cause of gum recession must be identified and addressed. There are many gum grafting surgical techniques whose suitability is dependent on different factors. Seek expert help from an experienced cosmetic dentist
If you want more information on gum grafts for treating gum recession, we can help! Get in touch and trust to answer all of your questions and help guide you towards the best direction in your oral health journey.
Luckily, you can secure a gum line recession consultation with Annex Dentistry – a leading Toronto general and cosmetic dentistry clinic with 50+ years of experience. Call: 416-962-4022. Alternatively, you can email [email protected] and start your journey to regaining a beautiful and healthy smile.
References
[1] MedicalNewsToday: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/312992
[2] Cleveland Clinic: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22753-gum-recession
[3] NCBI: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8156280/
[4] National Library of Medicine: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/326022#:~:text=Teeth%20grinding%20and%20clenching,-Some%20people%20grind&text=The%20motion%20of%20teeth%20grinding,gum%2C%20where%20bacteria%20can%20collect.
[5] Mouthhealthy: https://www.mouthhealthy.org/all-topics-a-z/womens-hormones-and-dental-health#:~:text=%E2%80%9CThe%20decreased%20estrogen%20that%20occurs,tooth%20at%20risk%20for%20decay.